Exercise-Induced Asthma, or Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction, is an affliction that affects the majority of people, particularly those who lead energetic lifestyles.
It is asthma attacks caused by vigorous physical activity, which requires proper documentation and coding of the affliction by medical practitioners.
This article aims to present the relevant ICD-10-CM codes for exercise-induced asthma, the importance of the codes in billing, and essential clinical information.
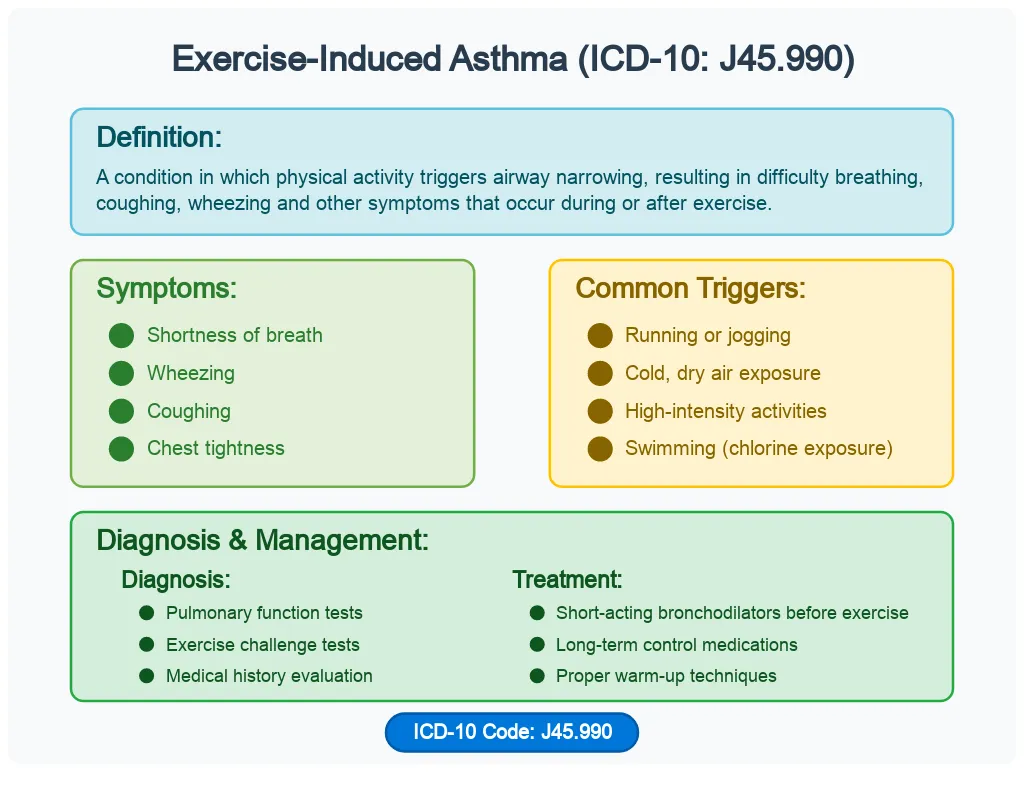
What is Exercise-Induced Asthma?
Exercise-Induced Asthma is linked to the below symptoms that occur during or after exercising: shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. These symptoms can seriously hinder one’s ability to exercise and engage in sports, which are very important for achieving ultimate levels of health and well-being.
Symptoms of Exercise-Induced Asthma
Symptoms often onset within a few minutes of starting exercise and typically last for about 10 to 15 minutes after activity has ceased. Cold dry air or high pollen conditions tend to exacerbate them, which is why having awareness of one’s trigger is useful.
Importance of Accurate Coding
Accurate coding of Exercise-Induced Asthma is necessary for clinical practice and billing. Accurate documentation of the condition by healthcare professionals is necessary to administer appropriate treatment and reimbursement. The following are the most commonly used ICD-10-CM codes for exercise-induced asthma:
Common ICD-10-CM Codes for Exercise-Induced Asthma
J45.990 – Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm
This is utilized specifically for asthma symptoms due to exercise. This is best utilized when patients come in with shortness of breath or wheezing during or after physical activity.
J45.909 – Unspecified Asthma, Uncomplicated
Use this general code when the exact type of asthma is not detailed but may be induced by exercise. This is utilized in cases when symptoms may not be readily placed in a single category.
J45.21 – Asthma with (Acute) Exacerbation
This is applied when an asthmatic patient with known asthma presents with an acute onset of symptoms, which may be precipitated due to exercise.
Which Exercise-Induced Asthma ICD Codes Are Billable?
All the ICD-10-CM codes that are listed under Exercise-Induced Asthma are generally billable. They are distinct medical conditions requiring treatment. Proper documentation must be made, however, especially when utilizing general codes like J45.909, to prevent inconsistencies and ensure proper billing.
Clinical Facts about Exercise-Induced Asthma
Patients and doctors need to be aware of Exercise-Induced Asthma. Some of the essentials to remember are:
Management and Prevention
Include a total warm-up before exercise and a cool-down afterwards. This can help reduce the probability of an asthma attack.
• Application of Inhalers: Inhalers or bronchodilators will be helpful when taken before exercise. These medications may stop the buildup of symptoms during exercise.
• Monitoring Symptoms: Appropriate monitoring of symptoms and consultation with a healthcare provider are essential. This can allow people to manage their condition and adjust exercise routines suitably.
Environmental Factors
Cold dry air as well as pollen counts may precipitate an exacerbation of the symptoms. The person needs to remain vigilant about such environmental factors and make suitable adjustments to their exercise routine.
Synonyms for Exercise-Induced Asthma
Exercise-induced asthma is also known by many other names, which can be used equally in clinical practice. These include:
• Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction
• Exercise-Associated Asthma
• Sports-Induced Asthma
• Workout-Triggered Asthma
• Physical Activity Induced Wheezing
It is useful for medical practitioners to know these synonyms while documenting the status of patients and giving overall treatment.
Bottom Line
Exercise-Induced Asthma is a worry for the majority who would love to maintain an active lifestyle. Proper coding using ICD-10-CM codes is necessary for effective management and adequate billing. J45.990, J45.909, and J45.21 are crucial codes for reporting the condition.
By being aware of the symptoms, management strategies, and importance of proper coding, patients and healthcare professionals can work together to incorporate exercise into a safe and enjoyable part of life.
If you experience symptoms of exercise-induced asthma, consult a healthcare professional to discuss your condition and how best to manage it. Keep in mind that staying active is crucial, and with some planning, you can continue exercising while controlling your asthma.